Varicose veins develop when one-way valves in your veins fail, allowing blood to pool within the vein. Because pooled blood has a greater tendency to clot, varicose veins can be indicators of dangerous blood clots.
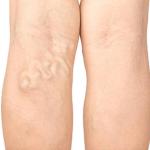
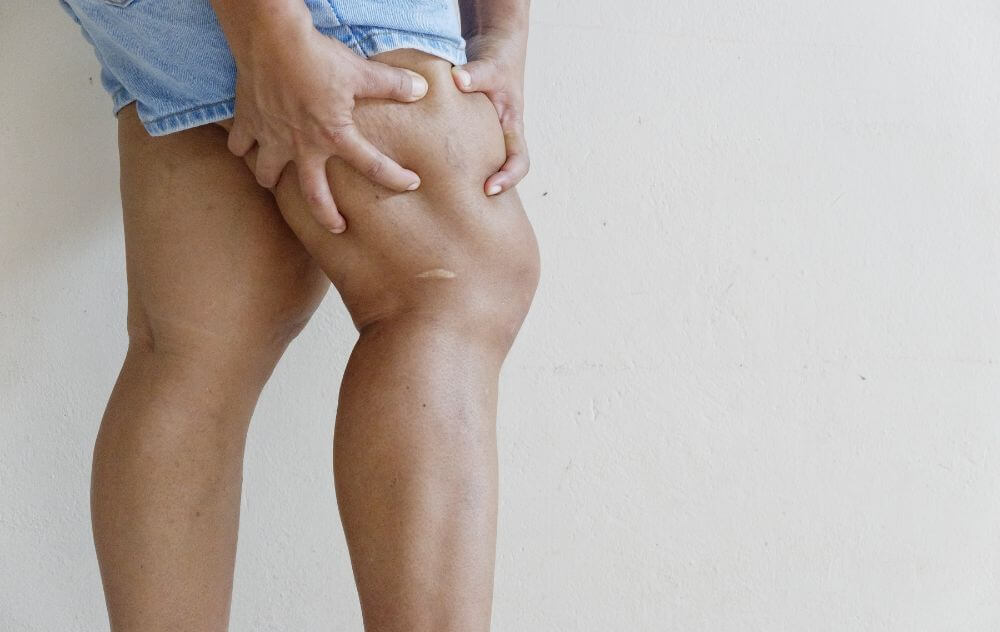
The first sign of varicose veins is a blue or purple, rope-like, bulging, or twisted vein under the surface of the skin, usually in the legs. Some people do not have any other symptoms, while others may experience pain, swelling, heaviness, and cramping in the legs. Sudden worsening of these symptoms or the appearance of new symptoms such as redness or skin discoloration may indicate that you have a blood clot in the veins. Blood clots can be life-threatening. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, seek urgent medical evaluation.
Our experts are often asked if varicose veins cause blood clots and if varicose veins and blood clots are related. In this article, we discuss everything you need to know about how these two conditions are related, including the warning signs of varicose veins and blood clots, as well as their causes, risk factors, and treatment options.
At USA Vein Clinics, we offer minimally invasive, office-based treatments that can alleviate painful venous symptoms and reduce the risk of dangerous blood clots. For additional information on varicose veins and blood clots, we recommend consulting a vein specialist.
Varicose Vein vs Blood Clot
Are varicose veins and blood clots related?
Yes: Varicose veins can increase your risk of developing blood clots. Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted, visible veins that occur when a valve in the vein fails, allowing blood to flow backward and pool. This pooling can allow platelets to clump together, forming a blood clot within the blood vessels.
We’ll examine the differences between a blood clot and varicose veins below.
Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins visible just under the surface of the skin. Although they can occur anywhere on the body, varicose veins usually develop on the legs, ankles, and feet. These visible veins are blue or purple, measuring three millimeters or more across. While varicose veins are not always bothersome, they can cause painful and uncomfortable symptoms, including leg swelling, cramping, and fatigue.
Varicose veins are a sign of underlying vein disease, or venous insufficiency. Vein disease has several risk factors, including age, genetics, and lifestyle. The condition develops when tiny, one-way vein valves are placed under strain and begin to malfunction, leading to blood flowing backward or pooling in place—most often in the lower extremities. When blood flow becomes sluggish, veins begin to expand.
Blood Clots
A blood clot is a semi-solid mass of blood cells and other substances that form in a blood vessel. Blood clots are a normal part of the body’s immune response and can help stop bleeding from injuries. However, sometimes blood clots form in areas where they are not needed, become too large, or break off and travel to other parts of the body.
Some of the most common causes of blood clots include:
- Injury to a blood vessel
- Surgery
- Prolonged immobility, such as after a long car ride or plane flight
- Certain medical conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, and obesity
- Use of certain medications, such as birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy
A blood clot can develop in the superficial (closest to the skin) or deep (beneath the muscle) veins. A clot that develops in the superficial veins is called superficial thrombophlebitis; a clot in the deep veins is called deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT is a potentially dangerous condition because it can lead to a pulmonary embolism, a life-threatening condition. A pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot in the deep venous system breaks off and travels to the lungs. When this occurs, it is considered a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment.
Do Varicose Veins Cause Blood Clots?
Varicose veins and venous blood clots are both symptoms of the same condition. Varicose veins develop when the valves in your veins become weak, known as vein disease or venous insufficiency. Instead of traveling to the heart, the blood in these veins flows backward and pools in the veins. Stagnant or sluggish blood flow can result in blood clots.
Vein disease is progressive, meaning its symptoms worsen over time. When varicose veins are left untreated, their presence can increase your risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
For personalized recommendations on how to prevent blood clots, consult a vein specialist. Minimally invasive vein treatment can reduce the likelihood of blood clots, treat painful varicose vein symptoms, and improve your quality of life.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins and Blood Clots
There are many potential varicose veins and blood clot symptoms. It’s important to understand the differences between them, since the two conditions require different types of treatment.
Varicose Vein Symptoms
Varicose vein symptoms tend to come on gradually, worsening over time. Common varicose veins symptoms in the legs include:
- Swelling: Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet often accompanies varicose veins. Your shoes and socks may feel tighter, or you may experience pain and discomfort in swollen areas.
- Cramping: Many people with varicose veins experience cramping, most often in the calves, thighs, or buttocks. This can occur during the day (impacting mobility) or at night (affecting sleep quality).
- Heaviness: If you have varicose veins, your legs may feel unusually heavy. Some people describe the feeling as similar to wearing weights around their ankles.
- Numbness: When blood circulation slows due to venous insufficiency, you may experience sensations of numbness, usually in the legs and feet.
- Itching and burning: Some patients experience itching or burning skin near varicose veins. While this can be mistaken for a dermatological issue, it is usually a sign of vein disease progression.
- Pain relief when legs are elevated: You may notice that propping up your feet alleviates your leg symptoms. This is a common early-stage symptom of venous insufficiency.
If you experience any of the warning signs of varicose veins, consult a vein specialist for a full evaluation.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Symptoms
DVT symptoms can develop suddenly, usually only affecting one side of the body. Common DVT symptoms include:
- Leg swelling on one side
- Warmth in the affected region
- Skin redness
- Pain, tenderness, or cramping in the leg, ankle, or foot
If you experience signs of deep vein thrombosis, seek urgent medical care. In some cases, DVT can lead to pulmonary embolism, a life-threatening condition.
Pulmonary Embolism Symptoms
- Coughing up blood
- Dizziness
- Sudden chest pain
- Heart palpitations
- Shortness of breath
If you experience symptoms of pulmonary embolism, call 911 immediately or head directly to the emergency room.
Types of Blood Clots
There are two main types of blood clots in the veins: superficial thrombophlebitis and deep vein thrombosis.
Superficial thrombophlebitis refers to a blood clot that develops in a superficial vein (a vein located near the skin’s surface). Symptoms can include pain, redness, and swelling. If you experience these symptoms, it is important to have a doctor evaluate your condition. The presence of superficial thrombophlebitis can place you at greater risk for DVT, so an appointment with a vein specialist is recommended.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious type of blood clot that develops in the deep venous system. Common symptoms, which usually only affect one side of the body, include leg swelling, warmth, skin redness, pain, tenderness, and cramping. Since DVT can lead to pulmonary embolism, urgent treatment is necessary.
Risk Factors of Developing Varicose Veins and Blood Clots
There are numerous risk factors for developing varicose veins and blood clots, including:
- Personal or family history: If you or a close family member has ever been diagnosed with varicose veins or DVT, you are considered at increased risk for additional venous issues.
- Prolonged sitting or standing: Long periods of sitting or standing, such as during travel or for certain types of jobs, can impact blood flow in the legs and lead to varicose veins and blood clots.
- Smoking: Smoking can impact the health of your veins, leading to vein disease, varicose veins, and DVT.
- Obesity: Excess body weight puts pressure on the leg veins and increases the risk of varicose veins and blood clots.
- Pregnancy: Women are more likely to develop varicose veins and/or DVT during pregnancy due to increased blood volume, an expanding uterus, and changing hormones.
- Age: While anyone can develop varicose veins and blood clots, people over 40 are more likely to do so.
- A recent accident or surgery: Lengthy bed rest can increase your risk of developing venous issues.
- Other underlying health conditions: Health issues like diabetes and high blood pressure increase your risk of varicose veins and blood clots.
In addition to the above risk factors for varicose veins and blood clots, the following risk factors can contribute to the development of deep vein thrombosis:
- Varicose veins: Individuals with varicose veins may be at increased risk of developing blood clots, including DVT.
- Cancer: Certain types of cancer and cancer treatments increase your likelihood of developing DVT.
If you have any of the above risk factors, it is important to keep a close eye on varicose veins and blood clot symptoms. You may also benefit from an evaluation by an experienced vein specialist.
Schedule a Consultation with USA Vein Clinics
If you are concerned about your vein health, we recommend consulting one of our leading vein specialists at USA Vein Clinics. We are happy to provide additional information on the differences between a blood clot and a varicose vein and to answer any questions you may have about vein disease. As the largest network of vein treatment clinics in the United States with over 168 convenient locations, we have a team of experienced doctors near you.
Our experts can quickly evaluate venous symptoms to determine whether you are experiencing a varicose vein or a blood clot. We generally aim to treat varicose veins proactively so that blood clots are unable to develop in the first place. To improve your overall vein health, just give us a call at 888.768.3467 or schedule an appointment online.