While blood clots are often associated with the legs, they can also develop in the feet. A blood clot in the foot can be difficult to recognize because its symptoms may resemble common foot conditions, such as muscle strain, arthritis, or plantar fasciitis.
Blood clotting naturally helps with injuries like cuts or scrapes. However, it can be a problem when it’s caused by vein disease. This condition, where veins become weakened or damaged, can cause blood pooling in the legs. This “idle” blood flow makes blood cells more likely to stick together, leading to painful clot formation.
If untreated, blood clots can pose a serious risk to your health. Understanding the signs of blood clots in the feet is especially important for adults over 50 and for people with risk factors such as limited mobility, vein disease, or a history of blood clots. It can also help you determine when to seek medical care and avoid complications.
How Can You Get a Blood Clot in the Foot?
Blood clots in the feet occur when blood thickens and forms a clot in a blood vessel. In vein disease, stagnant blood flow in damaged or weakened veins can trigger inflammation, increasing the likelihood of blood cells clumping and forming clots.
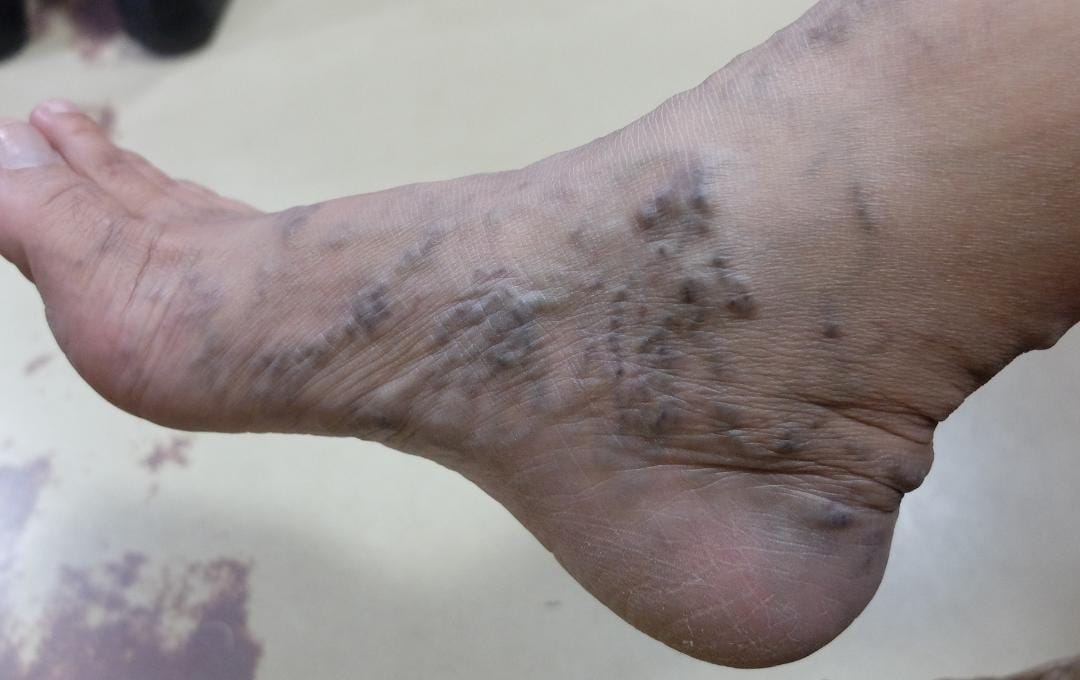
A blood clot in the foot is often mistaken for a common foot strain, but unlike a muscle injury, it is accompanied by localized warmth and redness. The location of the blood clot in the foot also matters: it can occur in the superficial veins near the skin or in the deeper plantar veins.
What You Should Know About Blood Clots
What Is DVT in the Feet?
DVT (deep vein thrombosis) is a specific type of blood clot that forms in a vein further inside the body. While it typically happens in the legs, DVT can also form in the plantar veins of the feet. This can cause significant pain and swelling, making walking difficult.
When you hear about DVT, you might assume it affects the calf or the thigh. However, as former NFL star and current football coach Deion Sanders’ publicized battle with blood clots illustrated, the feet are just as critical.
Plantar veins, which lie in the soles of your feet, feed into the posterior tibial veins behind your ankles. From there, blood in the posterior tibial veins travels up the calf and merges into the popliteal veins behind your knee. The blood then flows into larger deep veins, eventually reaching the heart.
This clear path can become dangerous if a DVT breaks off from the foot and travels toward the heart and lungs. When this happens, the clot is no longer a DVT, but a potentially life-threatening embolism. If an embolism blocks the arteries in the lungs, it can stop the flow of oxygen, strain the heart, and lead to heart failure, cardiac arrest, or death.
What Does a Blood Clot in the Foot Feel Like?
While sensations vary, many patients describe a foot with a blood clot feeling different from routine soreness.
Blood clot-related pain may feel:
- Tight or pressure-like
- Achy or throbbing
- Sharp and persistent
Unlike injury-related pain, symptoms of a blood clot in the foot may worsen over time and may not improve with rest, ice, compression, or elevation. The discomfort may also be localized to one foot rather than affecting both equally. This can feel different from a blood clot in the leg, which generally causes mild calf cramping and slight warmth or redness in a specific area of the leg, rather than pain concentrated in the foot itself.
How to Recognize Blood Clots in the Feet
Recognizing symptoms of blood clots in the feet can be challenging because they often mimic common injuries. However, it is vital to remain vigilant for changes in your feet, particularly if you have diabetes, high cholesterol, or varicose veins.
Common Blood Clot in Foot Symptoms Include:
- Swelling in one foot or ankle
- Warmth in the affected area
- Skin discoloration or redness
- Pain when standing or walking
- Tenderness along a vein
When to Seek Immediate Care
If you experience symptoms such as sudden swelling or warmth, seek emergency medical attention immediately, as acute clots require urgent hospital intervention.
However, if you aren’t in an emergency situation and notice persistent signs such as bulging veins, heaviness, or skin changes, these are often symptoms of vein disease. When blood pools in damaged veins, it significantly increases the risk of a blood clot forming over time. Treating these underlying vein issues is one of the most effective ways to lower your long-term risk of DVT.
It is important to note that blood clots can be “silent.” According to the National Institutes of Health, over 4% of patients with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) are asymptomatic. Don’t wait for a “silent” issue to become a crisis. Our specialists at USA Vein Clinics focus on treating vein disease to improve your circulation and peace of mind.
Schedule a Vascular Health Screening
DVT Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
| Risk Category | Specific Risk Factors | How to Reduce Your Risk |
| Mobility & Movement | • Bed rest from injury/surgery • Long periods of sitting (flights or desk jobs). |
• Flex your ankles while sitting • Take short walks every hour |
| Medical History | • Varicose veins • Vein disease • Age (50+) • Recent surgery (hip, knee, or foot) • Family history of vein issues. |
• Wear medical-grade compression stockings as recommended • Seek a vascular screening. |
| Physical Condition | • Obesity or extra weight | • Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on your veins. |
| Chemical & Hormonal | • Smoking (damages vein linings) • Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or birth control. |
• Work on a smoking cessation plan • Discuss clotting risks with your physician if on hormones. |
How USA Vein Clinics Can Help
Identifying circulatory issues early is the most effective way to protect your long-term health. Our vascular specialists focus on restoring proper blood flow through minimally invasive treatments, which directly reduces the risk of blood pooling and future clotting.
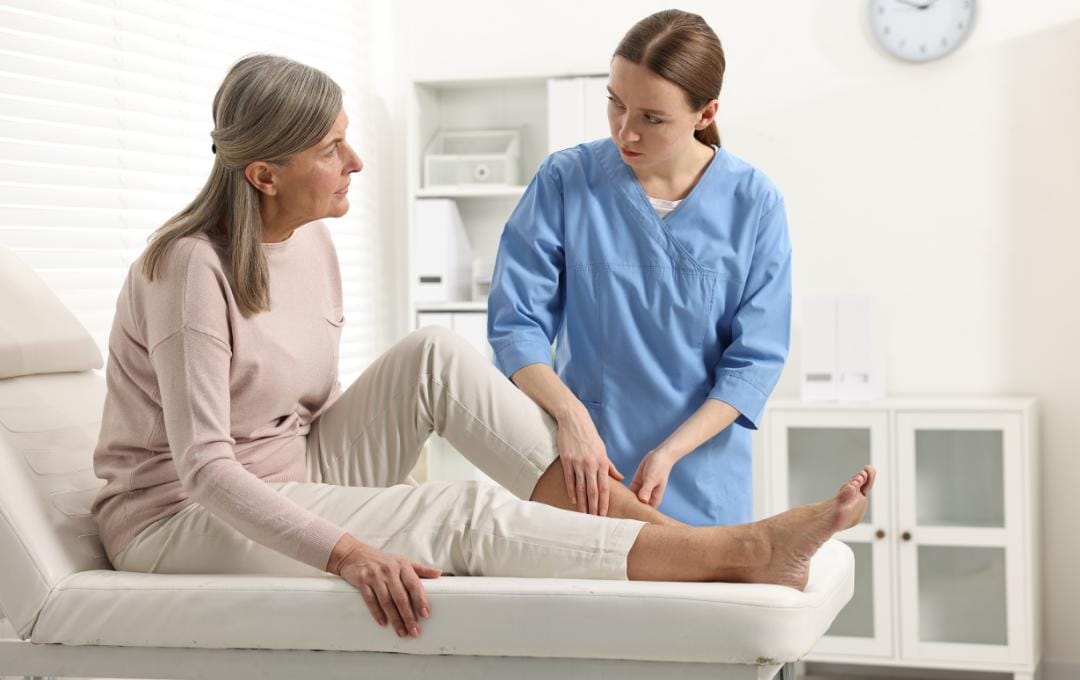
USA Vein Clinics specializes in diagnosing and treating underlying vein conditions that may contribute to poor circulation and increased risk of blood clots. Because symptoms of a blood clot in the foot can be subtle or easily mistaken for other foot issues, early evaluation by a vein specialist is an important step in protecting vascular health.
Our physicians are trained to identify venous disease before it progresses to more serious complications such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Through non-invasive evaluations, we provide patients with clarity, confirm the source of their symptoms, and create a personalized treatment plan to improve circulation and long-term peace of mind.
If you’re experiencing persistent foot pain, swelling, or changes in circulation, scheduling a consultation can help you take a proactive, informed step in your care.
FAQs About Blood Clots in the Feet
What does a blood clot in my foot feel like?
A blood clot in your foot may feel tight, achy, warm, or painful, especially when standing or walking. The discomfort often persists rather than improving with rest.
Do blood clots in the foot go away on their own?
Some small blood clots in the feet may resolve, but others can worsen and potentially turn into a pulmonary embolism–a life-threatening emergency. Medical evaluation is important to determine appropriate care.
What’s the difference between a bruise and a blood clot in the foot?
A bruise usually follows an injury and fades over time. A blood clot may cause ongoing pain, swelling, warmth, and skin changes without a clear cause.
Can a blood clot in your foot kill you?
If a blood clot dislodges from the vein and travels to the lungs, it can become a life-threatening embolism. Additionally, if a clot severely obstructs blood flow to the lower extremities for an extended period, it can lead to permanent tissue damage and, in extreme cases, require amputation. Early detection and treatment by a specialist are the most effective ways to reduce these risks.