When you think about the human body, you probably picture the heart pumping blood or the lungs filling with air. But behind the scenes, there’s an incredible network working just as hard: your veins.
Veins are part of the circulatory system and are responsible for carrying deoxygenated blood back to the heart. But exactly how many veins do we have? The answer is more fascinating than you might expect.
Overview of Blood Vessels in the Human Body
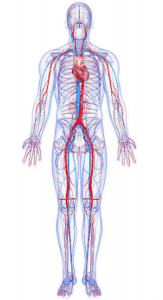
Your blood vessels are part of your body’s circulatory system. The heart is the center of the circulatory system, while vessels transport blood throughout the body. The total number of blood vessels in the human body cannot be counted. However, if all the blood vessels were removed from an adult’s body and laid straight, they would stretch almost 60,000 miles.
There are three types of blood vessels:
- Veins: Veins transport deoxygenated blood back to your heart. Valves in your vein ensure that blood only travels in one direction.
- Arteries: Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood from your heart to your organs and tissues.
- Capillaries: Capillaries are tiny vessels that connect arteries to veins and exchange nutrients, oxygen, and waste between the blood and body tissues.
The Role of Blood Vessels in Circulatory Health
The circulatory system fuels the body. To understand the role of the circulatory system, it can be helpful to think of the body as the car. The heart is the engine; the blood is the oil, and your vessels are the pipes, hoses, tubes, and wires. Similar to how a car should be maintained to run efficiently, it’s important to maintain healthy veins. The circulatory system delivers the essential nutrients and oxygen that keep organs functional. Conditions that affect it can be dangerous.
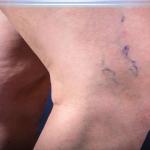
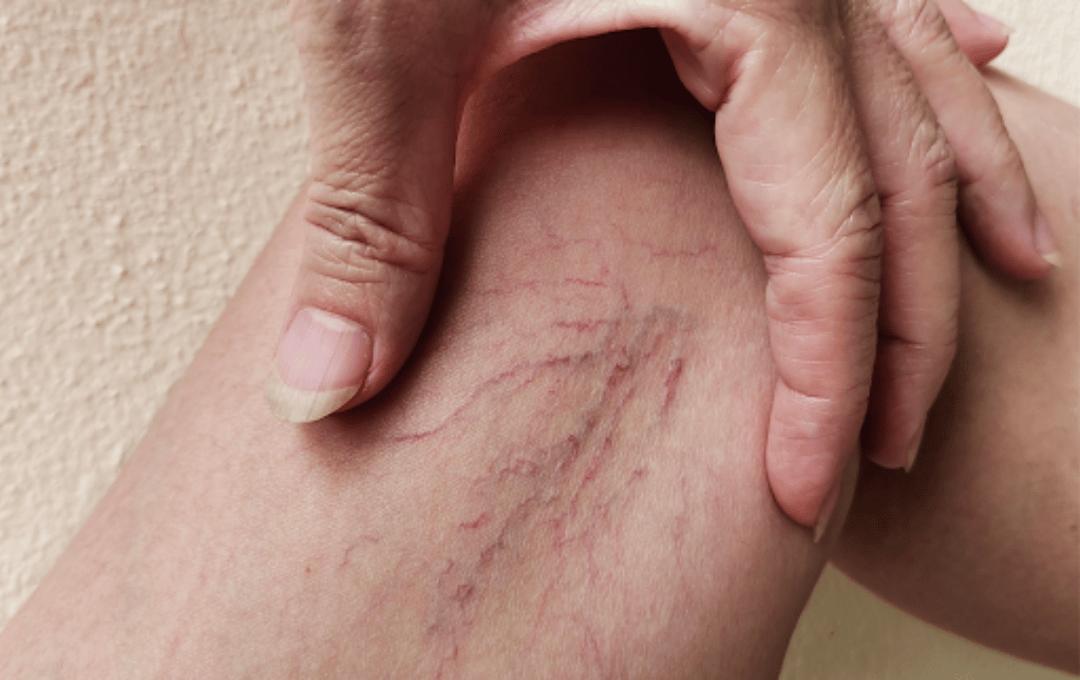
Vein disease is a condition of the circulatory system that is the underlying cause of varicose and spider veins. This common health condition can lead to a range of painful and uncomfortable symptoms. It can also place you at increased risk for serious health conditions such as blood clots and venous ulcers.
If you experience symptoms like swelling, cramping, itching, or fatigue in your legs, we recommend consulting a vein specialist as soon as possible.
So, How Many Veins Are There?
There’s no exact number, mainly because veins vary in size and branch endlessly throughout the body. However, experts estimate that the human body contains thousands of veins — from large, easily identifiable ones like the jugular vein in the neck to tiny venules that are microscopic.
In total, when you add up all your arteries, veins, and capillaries, you have about 60,000 miles of blood vessels inside you — enough to wrap around the Earth more than twice!
5 Questions to Evaluate Your Vein Health
Understanding Different Types of Veins
Veins come in different shapes and sizes, but they can generally be grouped into three main categories:
-
Deep veins: Located deep within the muscles, these veins are larger and often paired with arteries.
-
Superficial veins: Found closer to the surface of the skin, these veins are responsible for regulating body temperature and are often visible, especially in the arms and legs.
-
Pulmonary veins: These unique veins carry oxygen-rich blood from the lungs back to the heart.
Each of these types plays a crucial role in keeping your body functioning properly.
Why So Many Veins?
Your body needs so many veins to ensure every cell gets the nutrients and oxygen it needs — and to remove waste products. This dense network of blood vessels allows for rapid communication and resource distribution throughout your body, keeping you alive and healthy.
Common Vein Conditions
Since veins are so critical to health, problems can arise when they aren’t functioning properly. Some common vein issues include:
-
Varicose veins – Enlarged, twisted veins often visible on the legs
-
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) – A blood clot in a deep vein, typically in the legs
-
Chronic venous insufficiency – When veins struggle to send blood from the limbs back to the heart
Keeping your veins healthy through exercise, hydration, and regular medical checkups is key to maintaining good circulation.
Why Blood Vessel Health Matters
When blood vessel health is affected, the body is affected. Conditions such as vein disease impact circulation, which can cause painful symptoms such as:
When these conditions are untreated, they can lead to complications including:
- Venous Ulcers: These wounds take longer than a few months to heal or don’t heal at all. If the wound isn’t kept clean, it can become an infection.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): DVT is a condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a vein and blocks blood flow. These clots can travel to the lungs. DVT is potentially life-threatening.
- Superficial thrombophlebitis: Superficial thrombophlebitis is a blood clot that develops in a vein just under the skin. It can lead to pain and inflammation.
The only way to avoid these complications is to receive a diagnosis and treatment for vein disease. All treatments at USA Vein Clinics are FDA-approved and effective in reducing vein disease symptoms.
Stay on Top of Your Vein Health
Getting screened for vein disease is important if you are experiencing symptoms. Vein specialists at USA Vein Clinics offer comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans so you can focus on the care you need. Treating issues early can help reduce the risk of complications. With over 168 locations nationwide, you can find symptom relief when you call to schedule your appointment at a USA Vein Clinic near you.