Varicose vein bruising occurs when a vein ruptures or bleeds into the surrounding tissue. The sudden appearance of a bruised varicose vein can be alarming, especially if it develops without a clear cause.
When a varicose vein bruises, it can signal a deeper issue that can progress without treatment. Understanding why the bruising occurs and what causes varicose veins can help guide you toward appropriate evaluation and treatment.
What Is Varicose Vein Bruising?
Similar to common bruising, varicose vein bruising refers to bleeding from a weakened varicose vein into the surrounding tissues, leading to visible skin discoloration.
Varicose veins may bruise more easily than healthy veins because damaged vein valves allow blood to pool in the legs, increasing pressure within the vein. Over time, this pressure causes veins to swell, weaken, and become more susceptible to bleeding, especially after minor trauma.
In some cases, skin discoloration near a varicose vein may not be a bruise at all. The discoloration may be caused by venous stasis dermatitis, a chronic inflammatory condition linked to untreated vein disease. This condition can cause dry, flaky, or scaly skin. Patients also develop red or dark patches on the skin that may resemble a bruise.
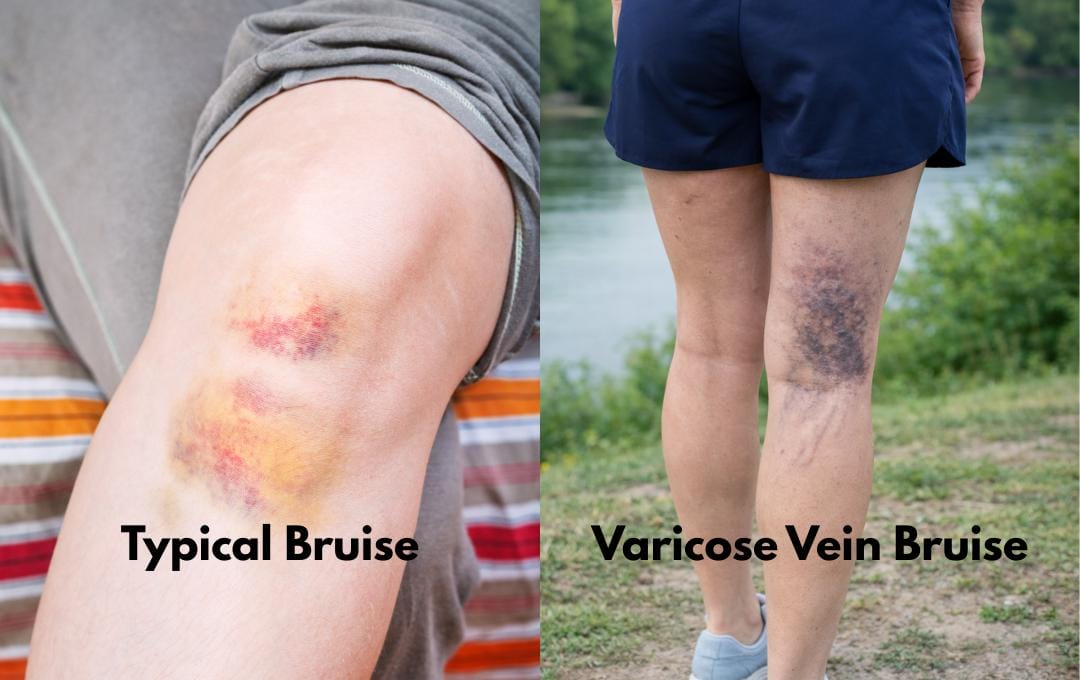
Common Bruises vs. Varicose Vein Bruises
While typical bruises and varicose vein bruises result from blood leaking into surrounding tissues, they often look different. A bruise from a varicose vein will be dark blue or purple in color and may change color as it heals.
Here are other ways to distinguish typical bruises from varicose vein bruises:
- A normal bruise usually disappears on its own after a few days to two weeks, while varicose vein bruises may take longer to resolve.
- Varicose vein bruises can appear without obvious pain or trauma.
- Varicose vein bruising can also cover a larger area of the skin than a standard bruise.
A varicose vein that bursts might also bleed externally, leading to sharp pain and discomfort.
Causes of Varicose Vein Bruising
Varicose vein bruising often develops after minor bumps or unnoticed trauma triggers bleeding beneath the skin, leading to visible discoloration. Other factors, such as blood thinners, aging skin, or certain medical conditions, can also make a person more susceptible to bruising.
Varicose veins are often weakened because of certain factors that increase the risk. Having high blood pressure and sitting for prolonged periods, for example, contributes to vein damage. This leads to blood pooling in the legs, adding pressure on the vein as it expands and twists. This can further weaken the vein and increase the risk of bruising.
Symptoms of Varicose Vein Bruising
Varicose vein bruising can cause similar symptoms to a common bruise, including:
- Skin discoloration
- Pain and tenderness
- Localized swelling
Bruised varicose veins may appear along with other symptoms, such as:
- Cramping, achiness, or restlessness
- Swelling
- Fatigue or heaviness
- Dry, itchy, or flaky skin
- Symptom relief after elevating the legs
Check Your Symptoms With a Quiz
Varicose Vein Bruise Risks
While a varicose vein bruise might appear to be a minor surface issue, it is often a visible warning sign of underlying chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) or vein disease. These bruises indicate that the vein walls are significantly weakened and under high pressure. Because bruising can be a precursor to more severe circulatory malfunctions, a professional evaluation by a vein specialist is essential to prevent the progression of vein disease. Left untreated, this underlying weakness increases the risk of:
Venous Ulcers
Venous ulcers are open sores that do not heal or take longer than six weeks to heal. The skin around an ulcer might be thickened or appear leathery, and the wound itself might bleed or ooze with a clear or yellowish discharge.
Blood Clots
People with varicose veins are at a higher risk for deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT is a type of blood clot that can become deadly if it breaks off from the veins in the leg and travels toward the lungs. If you notice symptoms such as skin that’s warm to the touch, redness around the area, or pain that feels like a pulled muscle or cramp, seek medical attention.
Bleeding
A varicose vein bruise can bleed externally if an injury causes the skin to break over the varicose vein. This can cause significant blood loss, and it increases the risk of future bleeding, according to the National Institutes of Health. Pressure and elevating your leg can slow down the flow of blood if your bruised vine bleeds. To reduce the risk of future bleeds, consult with a vein specialist to discuss vein treatment.
Treating Varicose Vein Bruises
While topical creams or cover-up makeup may temporarily conceal varicose vein bruising, they do not address the underlying vein condition that caused it. When bruising is recurrent or accompanied by other vein disease symptoms, an evaluation by a vein specialist can help identify and treat the problem rather than just its visible effects.
The USA Vein Clinics Approach
At USA Vein Clinics, we offer a full spectrum of vein care from consultations to treatment. Our physicians are experts in diagnosing and treating varicose veins, which often involves using advanced medical technology to locate vein damage and seal the vein shut.
Each treatment for varicose veins offered at USA Vein Clinics is minimally invasive. They can be done in the doctor’s office, and patients leave the same day with nothing more than an adhesive bandage. This often translates to a faster recovery period, so patients can resume normal activities within a day.
These treatments include:
- Endovenous laser therapy (EVLT)
- ClairVein®
- Varithena
- VenaSeal™
- Ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy
- Radiofrequency ablation
The 20-Year Difference in Specialized Care
Our physicians at USA Vein Clinics bring over 20 years of experience to the treatment of varicose veins, spider veins, and other signs of vein disease. As a trusted, national network of vein treatment centers, we’ve helped thousands of patients find better outcomes through personalized care plans.
Each clinic is formally recognized by the Intersocietal Accreditation Commission for Vascular Testing (IAC). Patients can expect gold-standard treatment when they come to seek relief from painful symptoms.
Book a consultation at a clinic near you today and learn how our vein treatments can help you.
Experience the Gold Standard of Care
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you know if a varicose vein has ruptured?
A ruptured varicose vein will bleed, causing blood to pool in the surrounding tissue. This will create a bruise under the skin. In some cases, a ruptured varicose vein can have a sudden, sharp pain or bleed externally. You might also notice some swelling around the affected area.
How is a varicose vein bruise different from hemosiderin staining?
Varicose vein bruises and hemosiderin staining both involve blood leaking into the skin, but they differ in cause and appearance. Bruising is temporary and related to injured veins, while hemosiderin staining occurs when iron leaks from tiny capillaries, causing longer-lasting brown or purple skin discoloration.
Can varicose veins bleed internally?
Yes, a varicose vein can bleed internally. If it does, you might see a bruise on the skin. If a bruise doesn’t go away after about two weeks, see a vein specialist for an evaluation.
Is it dangerous if you bruise a varicose vein?
It is not dangerous if you bruise a varicose vein. However, varicose veins could potentially be dangerous because they can progress into serious complications such as vein disease if untreated.