Have you heard of phlebitis? This term refers to the inflammation of a vein. Inflammation in veins occur when there is a blood clot in the vein or the vein walls are damaged.
Below, we take a closer look at what phlebitis is, what causes it, and how it can be treated.
What is Phlebitis?
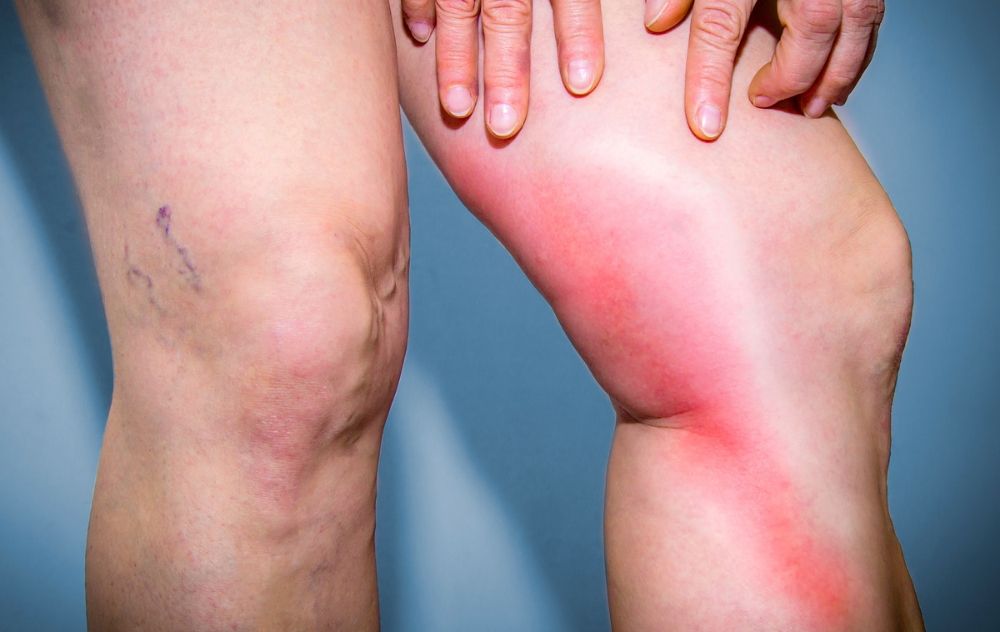
Phlebitis are veins that are inflamed, which are visibly red and painful. Phlebitis look like visibly red veins, and it is also referred to as thrombophlebitis, superficial thrombophlebitis, or superficial venous thrombosis.
Phlebitis symptoms can impact both deep veins and superficial veins near the skin’s surface. Most of the time, phlebitis occurs in the pelvis or legs when a blood clot forms in the veins. Because blood clots can lead to dangerous health issues, like embolisms, it’s important to recognize symptoms of phlebitis and seek medical evaluation when needed. Phlebitis symptoms are:
- Swelling
- Pain
- Warmth or tenderness
- Reddened skin (not always experienced)
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, reach out to a vein specialist who can diagnose and treat your phlebitis and varicose veins.
What Causes Phlebitis?
Phlebitis is an inflammatory process that causes a blood clot to form and block the veins, usually in your legs. Blood clots can form when the flow of blood in the veins slows or changes. Having another medical condition, like vein disease, puts you at an increased risk for phlebitis. Other risk factors that might cause phlebitis include:
- Smoking
- Taking estrogen or birth control pills
- Inactivity (usually sitting for extended periods of time)
- Family history of blood clots
- Pregnancy or giving birth in the past 6 months
- Being obese or overweight
- Fractures or traumatic injury to the pelvis or legs
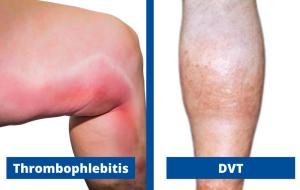
Phlebitis in the superficial venous system is called superficial thrombophlebitis, and when it affects a deep vein, it is referred to as deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Understanding the difference between deep vein thrombosis and phlebitis is important because DVT can cause life-threatening pulmonary embolism when a clot travels and blocks blood flow to the lungs.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) vs. Superficial Thrombophlebitis
The main difference between deep vein thrombosis and superficial thrombophlebitis is where the blood clot is located. As mentioned above, blood clots can form as a result of vein disease. Vein disease occurs when the valves in your veins malfunction and are unable to keep blood flowing from your legs back up to your heart. When your vein valves cannot effectively pump blood back to the heart, blood begins to pool in your legs, placing more pressure on the veins.
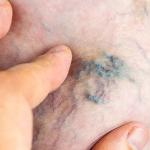
Blood collecting in your legs can cause varicose veins, which are bulging, twisted veins near the surface of the skin. Blood flow through varicose veins is slowed down due to increased pressure, and this often causes blood clots to form. These clots are called superficial thrombophlebitis because they form close to the surface of the skin. Sometimes, patients experience painful, hard lumps underneath the skin as a symptom of superficial thrombophlebitis. This condition is usually painful and can be treated to clear the blood clot and relieve the inflammation.
Superficial thrombophlebitis is rarely associated with life-threatening deep venous disease. Many vein experts say that they have not found enough evidence to suggest that phlebitis could be a risk factor for pulmonary embolism.
On the other hand, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when blood clots develop within the deep venous system. When a deep vein in the leg is affected by DVT, your leg may become swollen, painful, and tender to the touch. These symptoms occur most commonly in the calf, but may occur anywhere in the leg up to the groin.
When deep vein thrombosis is left untreated, it can lead to a dangerous condition, pulmonary embolism. . The blood clot can dislodge and travel through the circulatory system to the lungs, blocking blood flow. A pulmonary embolism is life-threatening and requires immediate medical treatment. However, for the best health outcomes, see a doctor right away if you have a red, swollen, or tender vein in your legs.
If you notice any of these symptoms, along with other symptoms of vein disease like varicose veins, the expert vein specialists at USA Vein Clinics can provide an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment recommendations. Our treatment options can relieve your pain and get you back to your daily activities without a long recovery time.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Phlebitis
If you have symptoms of phlebitis, your doctor will conduct a thorough physical examination. However, a vascular ultrasound is needed to confirm a phlebitis diagnosis and determine which veins are being affected by the blood clot. Ultrasound testing is crucial because, according to a 2021 study, 23% of patients with phlebitis also had DVT.
They might perform additional tests such as doppler ultrasound or venography. Doppler ultrasound allows your doctor to check the blood flow in your veins, whereas venography uses x-rays to display the veins inside the legs.
Once diagnosed, your doctor will discuss phlebitis treatment. Your doctor may recommend:
- Using compression socks
- Warm compresses
- Leg elevation when at rest
- Regular exercise to promote circulation and break up periods of inactivity
- Taking blood thinners
While these recommendations might help manage your pain and inflammation, seeking treatment can address the underlying cause of the blood clots and may prevent them from returning or developing into a more serious condition, like DVT.
Treatment of Phlebitis
Phlebitis and varicose veins are often interrelated. According to the National Center for Biotechnology Information, varicose veins are the most common factor in up to 88% of superficial thrombophlebitis cases. If you have varicose veins, treatment may help reduce your risks for superficial thrombophlebitis and DVT.
Blood clots occurring in superficial veins have a small chance of traveling to where these veins meet a deeper vein. If this happens, the blood clot could develop into DVT. Treating underlying vein disease can help prevent phlebitis and DVT.
Explore Your Options at USA Vein Clinics
At USA Vein Clinics, our doctors specialize in non-surgical procedures that can treat your varicose veins and may keep painful or dangerous blood clots from developing. Our treatments typically take less than 30 minutes, depending on the number of veins affected, and you can return to your normal routine after only a short recovery time. Your minimally invasive treatment options may include:
- Endovenous Laser Therapy (EVLT): Often considered the “gold standard” for treating vein disease, this procedure uses laser energy to heat and close the diseased veins. This is one of the quickest treatments available, taking around 15 minutes and allowing you to resume daily activities immediately.
- VenaSeal™: The latest technology for vein treatment, the VenaSeal™ procedure uses medical adhesive to provide immediate vein closure with minimal pain and discomfort. Following the procedure, you’ll only need a band-aid over the catheter insertion site.
To explore our full range of vein treatment options or see if treatment is covered by insurance, schedule an appointment online or give us a call at 888.768.3467. Our dedicated team is looking forward to working with you.
Medically Reviewed By
Dr. Yan Katsnelson is the founder and CEO of USA Vein Clinics. He is a highly skilled cardiac surgeon who completed a fellowship at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard School of Medicine, in Boston, MA. His clinical area of expertise includes minimally invasive procedures to treat vein and vascular diseases. Dr. Katsnelson has established himself as a strong advocate for accessible, affordable, and compassionate healthcare services.